看io.netty.util.concurrent.SingleThreadEventExecutor 代码时,发现执行execute() 方法时,会使用addTaskWakesUp标志判断是否需要唤醒线程。具体代码如下所示:
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {
startThread();
if (isShutdown()) {
boolean reject = false;
try {
if (removeTask(task)) {
reject = true;
}
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
// The task queue does not support removal so the best thing we can do is to just move on and
// hope we will be able to pick-up the task before its completely terminated.
// In worst case we will log on termination.
}
if (reject) {
reject();
}
}
}
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}查看资料,得知这是针对性的优化内容(https://github.com/netty/netty/commit/23d017849429c18e1890b0a5799e5262df4f269f),具体如下图红框所示:
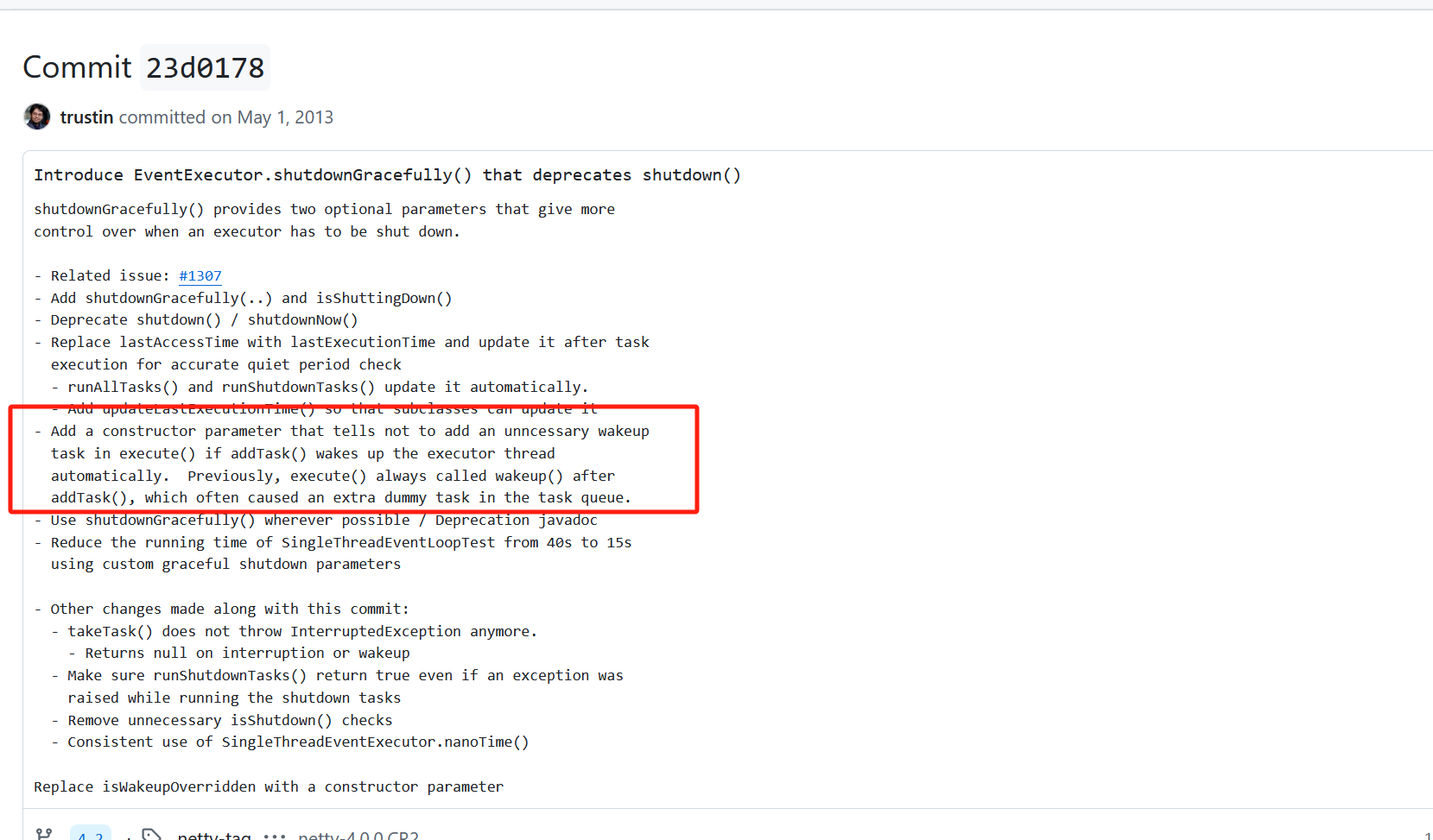
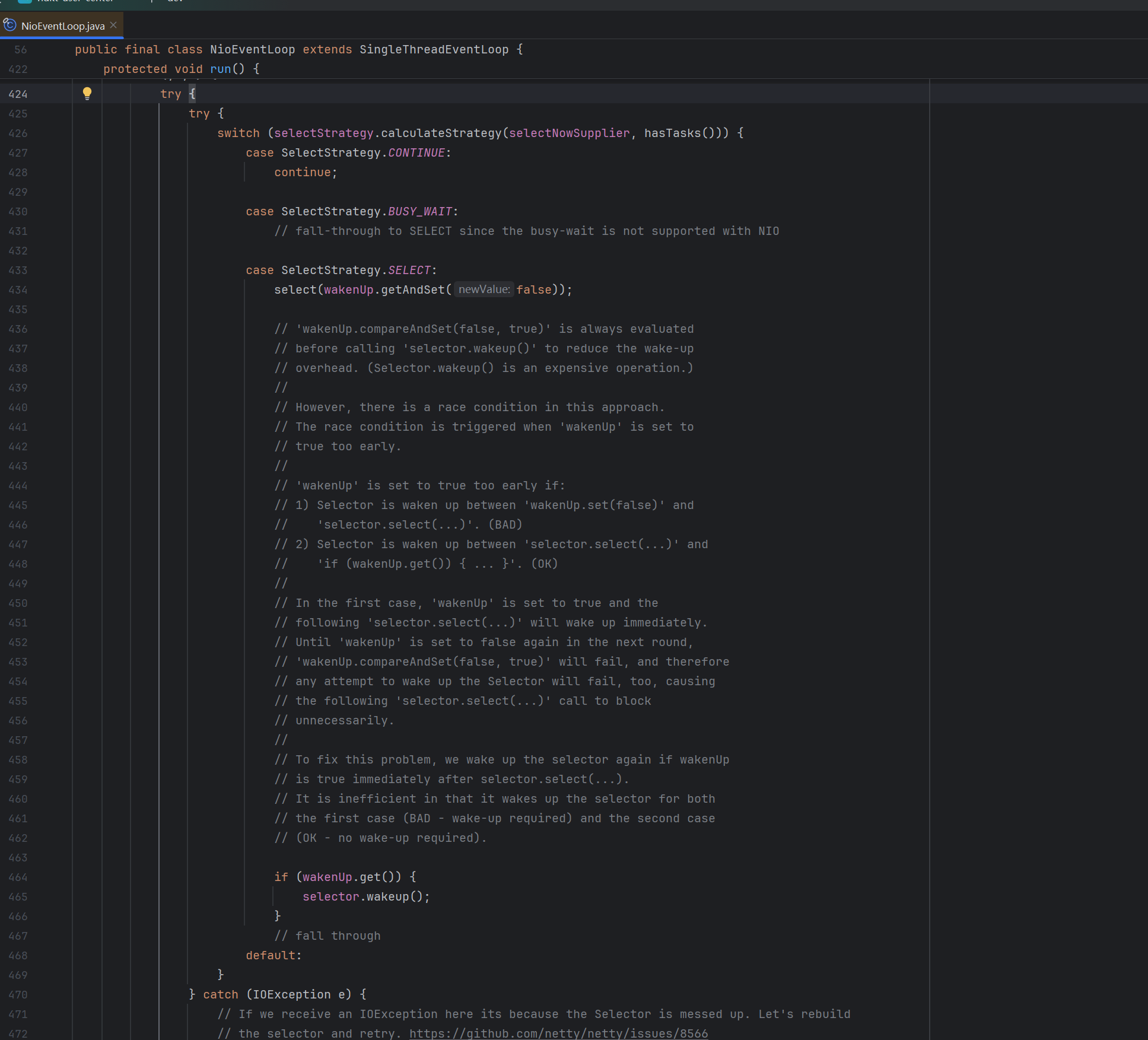
对于io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop类,其线程执行任务是基于Selector监听感兴趣的事件,当任务添加到taskQueue时,其线程是无法感知到的,因此需要调用wakeup(boolean inEventLoop) 以唤醒线程执行任务。
对于io.netty.channel.ThreadPerChannelEventLoop类(当前此类已废弃),其线程执行任务是基于监听taskQueue队列,所以当任务添加至taskQueue时,线程时可以感知到的,因此在执行完addTask()后无需追加执行wakeUp()操作。

